SIGNIFICANCE:
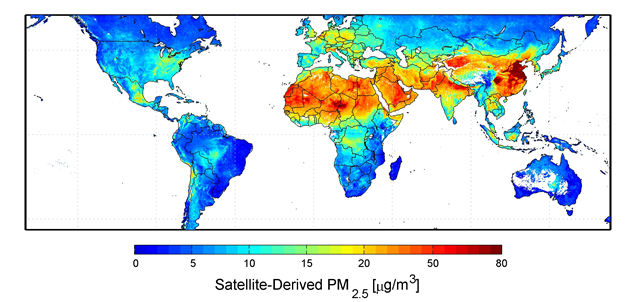
A satellite mapping analysis of PM2.5
concentration, as published by the US NASA lab, indicates the coastal areas of Eastern
China as the most affected by PM2.5 pollution in the world. According to
statistics from China's Ministry of Environmental Protection, cities in three
regions—Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta and Jing-Jin-Ji Region (Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei)
have seen over 100 smoggy days each year, with fine particle concentration two
to four times the level recommended by WHO Air Quality Guidelines[1]. This comes as a result of a continuous increase in coal burning and vehicle
usage. Investigations by the Chinese Academy of Engineering reveal the
above-mentioned air pollution of these cities are attributable to both soot and
vehicle tail gas. Because of their insatiable demand for energy, these cities have
been hit hard by air pollution[2].
References:
[1] Environment Planning Academy, Ministry of Environmental Protection, Guidance on Formulation of 12th Five-Year Plan of Atmospheric Pollution Joint Prevention and Control in Priority Regions.
[2] China's Energy Mid-Long Term Development Strategy Research--Environment, Science Press, February 2011.
[2] China's Energy Mid-Long Term Development Strategy Research--Environment, Science Press, February 2011.